数据库管理软件分类
- 关系型:如sqllite,db2,oracle,access,sql server,MySQL,注意:sql语句通用
- 非关系型:mongodb,redis,memcache
- 可以简单的理解为:关系型数据库需要有表结构,非关系型数据库是key-value存储的,没有表结构
mysql软件安装
一、Window版本
1.安装步骤
- 步骤1:下载:MySQL Community Server 5.7.16
- 步骤2:解压:如果想要让MySQL安装在指定目录,那么就将解压后的文件夹移动到指定目录,如:C:\mysql-5.7.16-winx64
- 步骤3:添加环境变量:【右键计算机】--》【属性】--》【高级系统设置】--》【高级】--》【环境变量】--》【在第二个内容框中找到 变量名为Path 的一行,双击】 --> 【将MySQL的bin目录路径追加到变值值中,用 ; 分割】
- 步骤4:初始化:mysqld --initialize-insecure
- 步骤5:启动MySQL服务:mysqld # 启动MySQL服务
- 步骤6:启动MySQL客户端并连接MySQL服务:mysql -u root -p # 连接MySQL服务器
2.制作MySQL的Windows服务
- 制作MySQL的Windows服务,在终端执行此命令:"c:\mysql-5.7.16-winx64\bin\mysqld" --install 注意:--install前,必须用绝对路径
- 移除MySQL的Windows服务,在终端执行此命令:"c:\mysql-5.7.16-winx64\bin\mysqld" --remove
- 注册成服务之后,以后再启动和关闭MySQL服务时,仅需执行如下命令:
- 启动MySQL服务:net start mysql 关闭MySQL服务:net stop mysql
mysql软件基本管理
一、windows平台下
1.忘记密码
- 关闭mysql服务
- 在cmd中执行:mysqld --skip-grant-tables
- 在cmd中执行:mysql
- 执行如下sql:
- update mysql.user set authentication_string=password('') where user = 'root';
- flush privileges;
- 杀死mysqld: tskill mysqld
- 重启mysql服务
2.配置文件my.ini
- 强调:配置文件中的注释可以有中文,但是配置项中不能出现中文
3.统一字符编码
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | #1. 修改配置文件 [mysqld] character - set - server = utf8 collation - server = utf8_general_ci [client] default - character - set = utf8 [mysql] default - character - set = utf8 #2. 重启服务 #3. 查看修改结果: #show variables like '%char%' |
存储引擎
- 存储引擎就是表的类型
- 查看MySQL支持的存储引擎show engines;
- 指定表类型/存储引擎:
- create table t1(id int)engine=innodb; #一般用这个
- create table t2(id int)engine=memory;
- create table t3(id int)engine=blackhole;
- create table t4(id int)engine=myisam;
操作库
一、基础操作
1、增
- create database db1 charset utf8;
2、删
- drop database db1;
3、改
- alter database db1 charset utf8;
4、查
- show databases;
- show create database db1;
- select database();
二、导入导出
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 | 1 、导出数据库数据: #语法: # mysqldump -h 服务器 -u用户名 -p密码 数据库名 > 备份文件.sql #示例: #单库备份 mysqldump - uroot - p123 db1 > db1.sql mysqldump - uroot - p123 db1 table1 table2 > db1 - table1 - table2.sql #多库备份 mysqldump - uroot - p123 - - databases db1 db2 mysql db3 > db1_db2_mysql_db3.sql #备份所有库 mysqldump - uroot - p123 - - all - databases > all .sql 2 、导入数据库数据: mysqldump - u root - p密码 数据库名称 < 文件路径 #方法一: [root@bubu backup] # mysql -uroot -p123 < /backup/all.sql #方法二: mysql> use db1; mysql> SET SQL_LOG_BIN = 0 ; mysql> source / root / db1.sql #注:如果备份/恢复单个库时,可以修改sql文件 DROP database if exists school; create database school; use school; 3 、执行导入文件: create database db5 mysqldump - u root - p - d db5 < db1.sql |
三、其他操作
- use db1 #选择数据库
操作表
一、基础操作
1、增
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 | create table 表名( 字段名 1 类型[(宽度) 约束条件], 字段名 2 类型[(宽度) 约束条件], 字段名 3 类型[(宽度) 约束条件] )engine = innodb default charset = utf8; #注意:表中的最后一个字段不要加逗号 |
2、删
- drop table t1; #删表
- delete from t1;#清空表 #对于自增的字段,在用delete删除后,再插入值,该字段仍按照删除前的位置继续增长
- truncate t1 #应该用truncate清空表,比起delete一条一条地删除记录,truncate是直接清空表,在删除大表时用它
3、改
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 | 语法: 1. 修改表名 alter table 表名 rename 新表名; 2. 增加字段 alter table 表名 add 字段名 数据类型 [完整性约束条件…], add 字段名 数据类型 [完整性约束条件…]; alter table 表名 add 字段名 数据类型 [完整性约束条件…] FIRST; alter table 表名 add 字段名 数据类型 [完整性约束条件…] AFTER 字段名; 3. 删除字段 alter table 表名 drop 字段名; 4. 修改字段 alter table 表名 modify 字段名 数据类型 [完整性约束条件…]; alter table 表名 change 旧字段名 新字段名 旧数据类型 [完整性约束条件…]; alter table 表名 change 旧字段名 新字段名 新数据类型 [完整性约束条件…]; 示例: 1. 修改存储引擎 mysql> alter table t1 - > engine = innodb; 2. 添加字段 mysql> alter table t1 - > add name varchar( 20 ) not null, - > add age int ( 3 ) not null default 22 ; mysql> alter table t1 - > add stu_num varchar( 10 ) not null after name; / / 添加name字段之后 mysql> alter table t1 - > add sex enum( 'male' , 'female' ) default 'male' first; / / 添加到最前面 3. 删除字段 mysql> alter table t1 - > drop sex; mysql> alter table t1 - > drop mac; 4. 修改字段类型modify mysql> alter table t1 - > modify age int ( 3 ); mysql> alter table t1 - > modify id int ( 11 ) not null primary key auto_increment; / / 修改为主键 5. 增加约束(针对已有的主键增加auto_increment) mysql> alter table t1 modify id int ( 11 ) not null primary key auto_increment; ERROR 1068 ( 42000 ): Multiple primary key defined mysql> alter table t1 modify id int ( 11 ) not null auto_increment; Query OK, 0 rows affected ( 0.01 sec) Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0 6. 对已经存在的表增加复合主键 mysql> alter table t1 - > add primary key(host_ip,port); 7. 增加主键 mysql> alter table t1 - > modify name varchar( 10 ) not null primary key; 8. 增加主键和自动增长 mysql> alter table t1 - > modify id int not null primary key auto_increment; 9. 删除主键 a. 删除自增约束 mysql> alter table t1 modify id int ( 11 ) not null; b. 删除主键 mysql> alter table t1 - > drop primary key; |
4、查
- desc t1; #查看表结构
- show create table t1\G; #查看表详细结构,可加\G
- show tables;
二、其他操作
1.复制表
- 复制表结构+记录 (key不会复制: 主键、外键和索引): create table new_service select * from service;
- 只复制表结构: create table new1_service select * from service where 1=2;
- create table t4 like t1;
三、数据类型
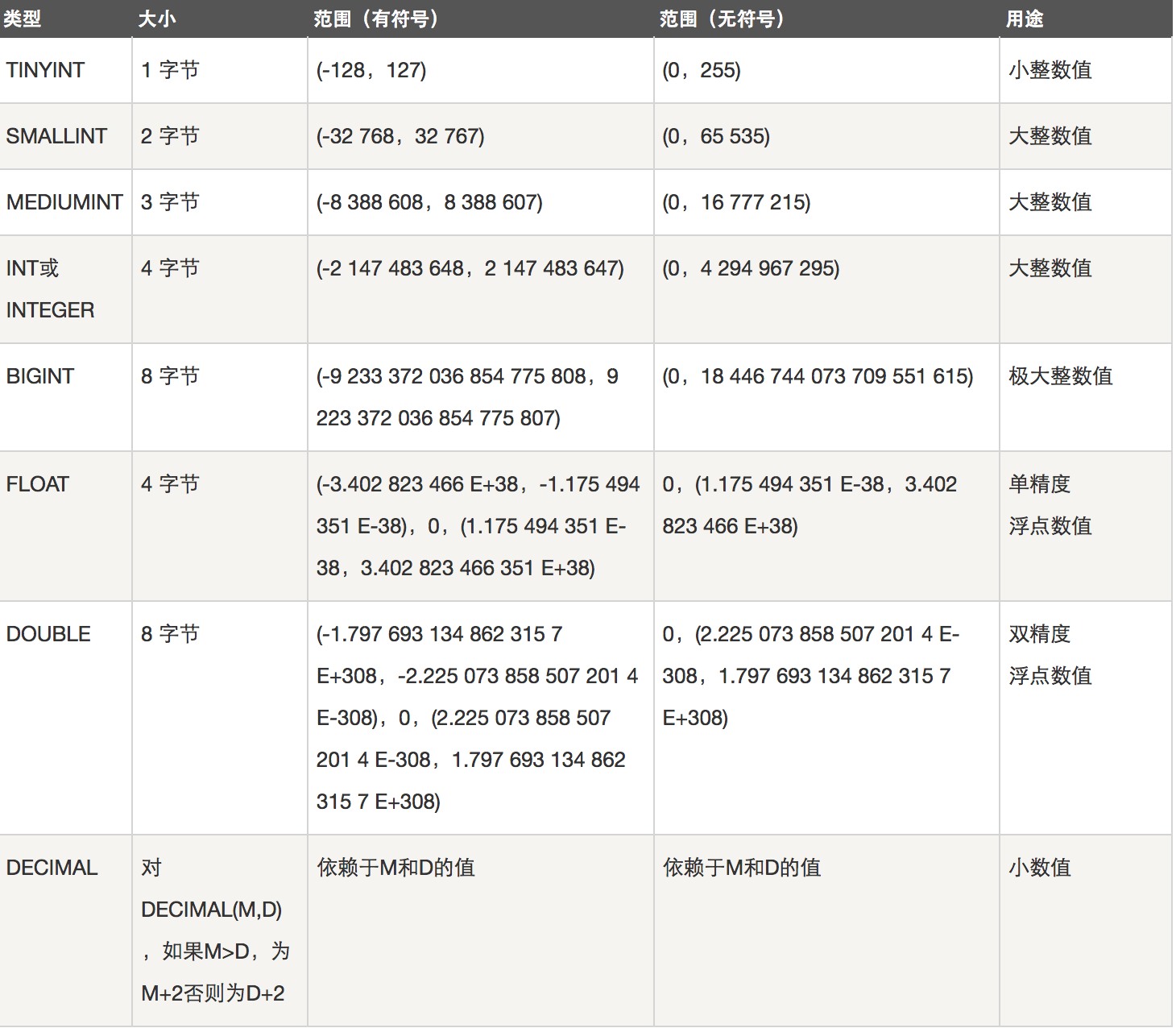
1、整数类型
- 整数类型:TINYINT SMALLINT MEDIUMINT INT BIGINT
- 作用:存储年龄,等级,id,各种号码等
- 注意:为该类型指定宽度时,仅仅只是指定查询结果的显示宽度,与存储范围无关。其实没有必要指定显示宽度,使用默认的就ok
2、浮点型
- 定点数类型 DEC等同于DECIMAL
- 浮点类型:FLOAT DOUBLE
- 作用:存储薪资、身高、体重、体质参数等
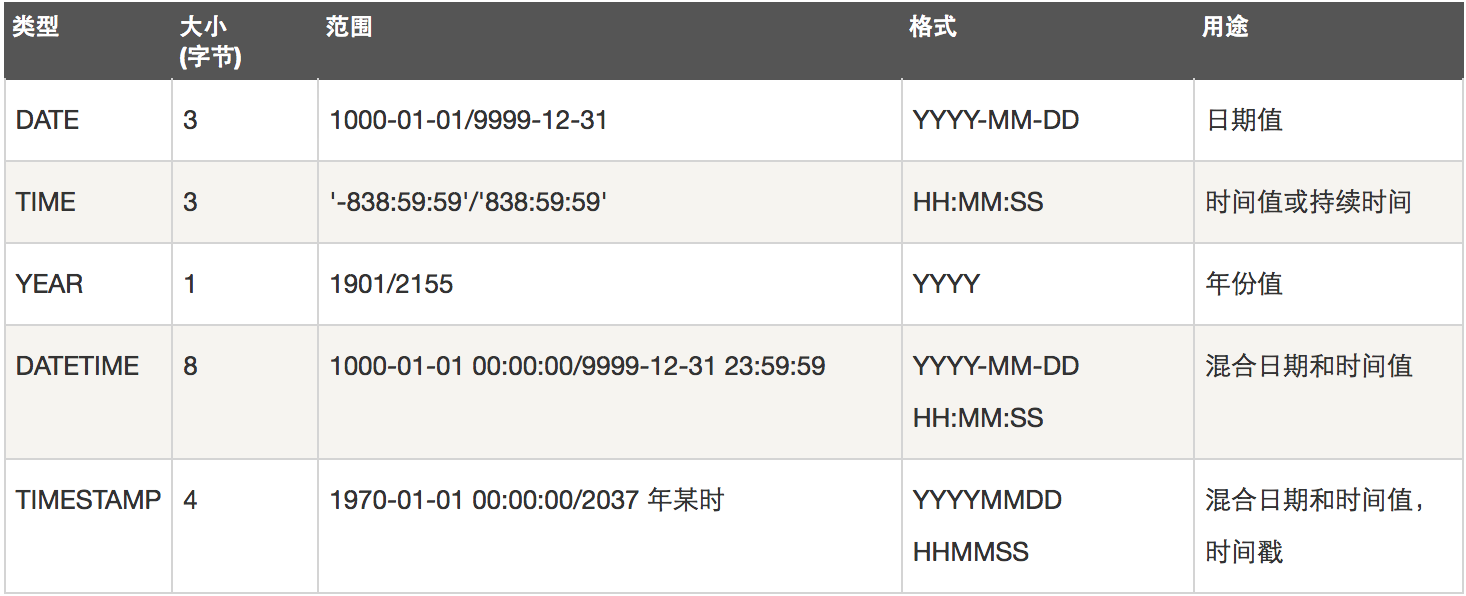
3、日期类型
- DATE TIME DATETIME TIMESTAMP YEAR
- DATETIME的日期范围是1001——9999年,TIMESTAMP的时间范围是1970——2038年。
- 作用:存储用户注册时间,文章发布时间,员工入职时间,出生时间,过期时间等
- create table t1(x datetime not null default now()); # 需要指定传入空值时默认取当前时间
- create table t2(x timestamp); # 无需任何设置,在传空值的情况下自动传入当前时间
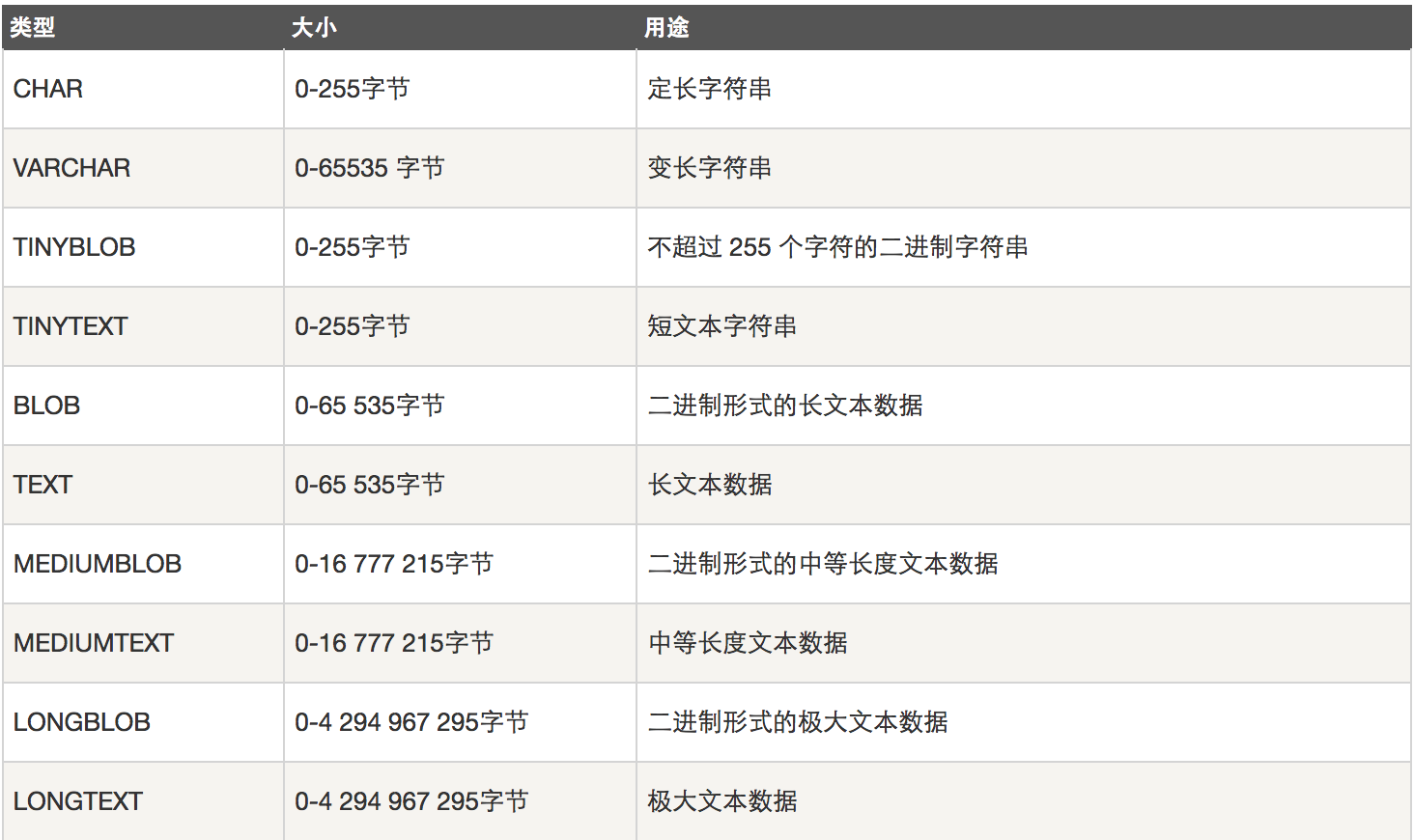
4、字符串类型
- 官网:
- 注意:char和varchar括号内的参数指的都是字符的长度
- char类型:定长,简单粗暴,浪费空间,存取速度快
- varchar类型:变长,精准,节省空间,存取速度慢
- text类型:用于保存变长的大字符串
- length:查看字节数,char_length:查看字符数
5、枚举类型与集合类型
- 字段的值只能在给定范围中选择,如单选框,多选框
- enum 单选 只能在给定的范围内选一个值,如性别 sex 男male/女female sex enum('male','female','保密'), #在指定范围内,多选一
- set 多选 在给定的范围内可以选择一个或一个以上的值(爱好1,爱好2,爱好3...) hobby set('play','music','read','study') #在指定范围内,多选多
四、表完整性约束
约束条件与数据类型的宽度一样,都是可选参数,作用:用于保证数据的完整性和一致性
- 是否是key: 主键: primary key 外键: foreign key 索引:(index,) 唯一:unique key (uk)
- 是否允许为空,默认null,可设置not null,字段不允许为空,必须赋值,或者也可以自动添加默认值 not null defalut 2
- 无符号unsigned
- 使用0填充 zerofill
1、unsigned
- age int unsigned NOT NULL default 20,
2、not null与default
- age int not null defalut 18,
- age int not null,
3、unique
- #方法1:在某一个字段后用unique: name varchar(20) unique,
- #方法2:在所有字段后单独定义unique: constraint uk_name unique(name) #创建唯一并为其命名uk_name
- #联合唯一:在所有字段后单独定义unique: unique(host,port)
4、primary key
- #方法1:not null+unique: id int not null unique, #主键
- #方法2:在某一个字段后用primary key : id int primary key, #主键
- #方法3:在所有字段后单独定义primary key: constraint pk_name primary key(id); #创建主键并为其命名pk_name
- #多列做主键:在所有字段后单独定义primary key: primary key(ip,port)
5、auto_increment
- 约束字段为自动增长,被约束的字段必须同时被key约束
- id int primary key auto_increment,#primary key auto_increment一般一起使用
6、foreign key
- 多对一:关联方式:foreign key
- 多对多:关联方式:foreign key + 一张新的表
- 一对一:关联方式:foreign key+unique
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 | """ 多对一:关联方式:foreign key 多对多:关联方式:foreign key + 一张新的表 一对一:关联方式:foreign key+unique =====================多对一===================== create table press( id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(20) ); create table book( id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(20), press_id int not null, foreign key(press_id) references press(id) on delete cascade on update cascade #一个出版社可以出版多本书 ); =====================多对多===================== create table author( id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(20) ); create table book( id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(20), ); #这张表就存放作者表与书表的关系,即查询二者的关系查这表就可以了 create table author2book( id int not null unique auto_increment, author_id int not null, book_id int not null, constraint fk_author foreign key(author_id) references author(id) on delete cascade on update cascade, #===多对多==== constraint fk_book foreign key(book_id) references book(id) on delete cascade on update cascade, #===多对多==== primary key(author_id,book_id) ); =====================一对一===================== create table customer( id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(20) not null, qq varchar(10) not null, phone char(16) not null ); create table student( id int primary key auto_increment, class_name varchar(20) not null, customer_id int unique, #该字段一定要是唯一的 foreign key(customer_id) references customer(id) #外键的字段一定要保证unique on delete cascade on update cascade ); """ |
操作记录
一、基础操作
1、增
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 | 1. 插入完整数据(顺序插入) 语法一: INSERT INTO 表名(字段 1 ,字段 2 ,字段 3 …字段n) VALUES(值 1 ,值 2 ,值 3 …值n); 语法二: INSERT INTO 表名 VALUES (值 1 ,值 2 ,值 3 …值n); 2. 指定字段插入数据 语法: INSERT INTO 表名(字段 1 ,字段 2 ,字段 3 …) VALUES (值 1 ,值 2 ,值 3 …); 3. 插入多条记录 语法: INSERT INTO 表名 VALUES (值 1 ,值 2 ,值 3 …值n), (值 1 ,值 2 ,值 3 …值n), (值 1 ,值 2 ,值 3 …值n); 4. 插入查询结果 语法: INSERT INTO 表名(字段 1 ,字段 2 ,字段 3 …字段n) SELECT (字段 1 ,字段 2 ,字段 3 …字段n) FROM 表 2 WHERE …; |
2、删
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | 语法: DELETE FROM 表名 WHERE CONITION; 示例: DELETE FROM mysql.user WHERE password = ’’; |
3、改
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | 语法: UPDATE 表名 SET 字段 1 = 值 1 , 字段 2 = 值 2 , WHERE CONDITION; 示例: UPDATE mysql.user SET password = password(‘ 123 ’) where user = ’root’ and host = ’localhost’; |
4、查
①单表
1):单表查询的语法
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 | SELECT DISTINCT 字段 1 ,字段 2. .. FROM 表名 WHERE 条件 GROUP BY field HAVING 筛选 ORDER BY field LIMIT 限制条数 |
2):关键字的执行优先级
- -> from -> where -> group by-> having-> select-> distinct-> order by-> limit
- 1.找到表:from
- 连表的情况
- 1.1 on 执行on过滤
- 1.2 join 添加外部行
- 2.拿着where指定的约束条件,去文件/表中取出一条条记录
- 3.将取出的一条条记录进行分组group by,如果没有group by,则整体作为一组
- 4.将分组的结果进行having过滤
- 5.执行select
- 6.去重distinct
- 7.将结果按条件排序:order by
- 8.限制结果的显示条数
3):简单查询
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 | company.employee 员工 id id int 姓名 emp_name varchar 性别 sex enum 年龄 age int 入职日期 hire_date date 岗位 post varchar 职位描述 post_comment varchar 薪水 salary double 办公室 office int 部门编号 depart_id int #创建表 create table employee( id int not null unique auto_increment, name varchar( 20 ) not null, sex enum( 'male' , 'female' ) not null default 'male' , #大部分是男的 age int ( 3 ) unsigned not null default 28 , hire_date date not null, post varchar( 50 ), post_comment varchar( 100 ), salary double( 15 , 2 ), office int , #一个部门一个屋子 depart_id int ); #查看表结构 mysql> desc employee; + - - - - - - - - - - - - - - + - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - + - - - - - - + - - - - - + - - - - - - - - - + - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - + | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | + - - - - - - - - - - - - - - + - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - + - - - - - - + - - - - - + - - - - - - - - - + - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - + | id | int ( 11 ) | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment | | name | varchar( 20 ) | NO | | NULL | | | sex | enum( 'male' , 'female' ) | NO | | male | | | age | int ( 3 ) unsigned | NO | | 28 | | | hire_date | date | NO | | NULL | | | post | varchar( 50 ) | YES | | NULL | | | post_comment | varchar( 100 ) | YES | | NULL | | | salary | double( 15 , 2 ) | YES | | NULL | | | office | int ( 11 ) | YES | | NULL | | | depart_id | int ( 11 ) | YES | | NULL | | + - - - - - - - - - - - - - - + - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - + - - - - - - + - - - - - + - - - - - - - - - + - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - + #插入记录 #三个部门:教学,销售,运营 insert into employee(name,sex,age,hire_date,post,salary,office,depart_id) values ( 'egon' , 'male' , 18 , '20170301' , '老男孩驻沙河办事处外交大使' , 7300.33 , 401 , 1 ), #以下是教学部 ( 'alex' , 'male' , 78 , '20150302' , 'teacher' , 1000000.31 , 401 , 1 ), ( 'wupeiqi' , 'male' , 81 , '20130305' , 'teacher' , 8300 , 401 , 1 ), ( 'yuanhao' , 'male' , 73 , '20140701' , 'teacher' , 3500 , 401 , 1 ), ( 'liwenzhou' , 'male' , 28 , '20121101' , 'teacher' , 2100 , 401 , 1 ), ( 'jingliyang' , 'female' , 18 , '20110211' , 'teacher' , 9000 , 401 , 1 ), ( 'jinxin' , 'male' , 18 , '19000301' , 'teacher' , 30000 , 401 , 1 ), ( '成龙' , 'male' , 48 , '20101111' , 'teacher' , 10000 , 401 , 1 ), ( '歪歪' , 'female' , 48 , '20150311' , 'sale' , 3000.13 , 402 , 2 ), #以下是销售部门 ( '丫丫' , 'female' , 38 , '20101101' , 'sale' , 2000.35 , 402 , 2 ), ( '丁丁' , 'female' , 18 , '20110312' , 'sale' , 1000.37 , 402 , 2 ), ( '星星' , 'female' , 18 , '20160513' , 'sale' , 3000.29 , 402 , 2 ), ( '格格' , 'female' , 28 , '20170127' , 'sale' , 4000.33 , 402 , 2 ), ( '张野' , 'male' , 28 , '20160311' , 'operation' , 10000.13 , 403 , 3 ), #以下是运营部门 ( '程咬金' , 'male' , 18 , '19970312' , 'operation' , 20000 , 403 , 3 ), ( '程咬银' , 'female' , 18 , '20130311' , 'operation' , 19000 , 403 , 3 ), ( '程咬铜' , 'male' , 18 , '20150411' , 'operation' , 18000 , 403 , 3 ), ( '程咬铁' , 'female' , 18 , '20140512' , 'operation' , 17000 , 403 , 3 ) ; #ps:如果在windows系统中,插入中文字符,select的结果为空白,可以将所有字符编码统一设置成gbk |
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 | #简单查询 SELECT id ,name,sex,age,hire_date,post,post_comment,salary,office,depart_id FROM employee; SELECT * FROM employee; SELECT name,salary FROM employee; #避免重复DISTINCT SELECT DISTINCT post FROM employee; #通过四则运算查询 SELECT name, salary * 12 FROM employee; SELECT name, salary * 12 AS Annual_salary FROM employee; SELECT name, salary * 12 Annual_salary FROM employee; #定义显示格式 CONCAT() 函数用于连接字符串 SELECT CONCAT( '姓名: ' ,name, ' 年薪: ' , salary * 12 ) AS Annual_salary FROM employee; CONCAT_WS() 第一个参数为分隔符 SELECT CONCAT_WS( ':' ,name,salary * 12 ) AS Annual_salary FROM employee; 结合CASE语句: SELECT ( CASE WHEN NAME = 'tom' THEN NAME WHEN NAME = 'rose' THEN CONCAT(name, '_VIP' ) ELSE concat(NAME, 'COMMON' ) END ) as new_name FROM emp; |
4):WHERE约束
- where字句中可以使用:
- 1. 比较运算符:> < >= <= <> !=
- 2. between 80 and 100 值在10到20之间
- 3. in(80,90,100) 值是10或20或30
- 4. like 'egon%' pattern可以是%或_, %表示任意多字符 , _表示一个字符
- 5. 逻辑运算符:在多个条件直接可以使用逻辑运算符 and or not
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 | #1:单条件查询 SELECT name FROM employee WHERE post = 'sale' ; #2:多条件查询 SELECT name,salary FROM employee WHERE post = 'teacher' AND salary> 10000 ; #3:关键字BETWEEN AND SELECT name,salary FROM employee WHERE salary BETWEEN 10000 AND 20000 ; SELECT name,salary FROM employee WHERE salary NOT BETWEEN 10000 AND 20000 ; #4:关键字IS NULL(判断某个字段是否为NULL不能用等号,需要用IS) SELECT name,post_comment FROM employee WHERE post_comment IS NULL; SELECT name,post_comment FROM employee WHERE post_comment IS NOT NULL; SELECT name,post_comment FROM employee WHERE post_comment = ' '; 注意' '是空字符串,不是null ps: 执行 update employee set post_comment = '' where id = 2 ; 再用上条查看,就会有结果了 #5:关键字IN集合查询 SELECT name,salary FROM employee WHERE salary = 3000 OR salary = 3500 OR salary = 4000 OR salary = 9000 ; SELECT name,salary FROM employee WHERE salary IN ( 3000 , 3500 , 4000 , 9000 ) ; SELECT name,salary FROM employee WHERE salary NOT IN ( 3000 , 3500 , 4000 , 9000 ) ; #6:关键字LIKE模糊查询 通配符’ % ’ SELECT * FROM employee WHERE name LIKE 'eg%' ; 通配符’_’ SELECT * FROM employee WHERE name LIKE 'al__' ; |
5):分组查询:GROUP BY
- 1、首先明确一点:分组发生在where之后,即分组是基于where之后得到的记录而进行的
- 2、分组指的是:将所有记录按照某个相同字段进行归类,比如针对员工信息表的职位分组,或者按照性别进行分组等
- 3、为何要分组呢?取每个部门的最高工资?取每个部门的员工数?取男人数和女人数?
- 小窍门:‘每’这个字后面的字段,就是我们分组的依据
- 4、大前提:可以按照任意字段分组,但是分组完毕后,比如group by post,只能查看post字段,如果想查看组内信息,需要借助于聚合函数
- 5. 聚合函数 sum avg min max count
- 6. GROUP BY关键字和GROUP_CONCAT()函数一起使用
- 7. 如果我们用unique的字段作为分组的依据,则每一条记录自成一组,这种分组没有意义
- 8:ONLY_FULL_GROUP_BY #设置成功后,一定要退出,然后重新登录方可生效
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 | #查看MySQL 5.7默认的sql_mode如下: mysql> select @@ global .sql_mode; ONLY_FULL_GROUP_BY,STRICT_TRANS_TABLES,NO_ZERO_IN_DATE,NO_ZERO_DATE,ERROR_FOR_DIVISION_BY_ZERO,NO_AUTO_CREATE_USER,NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION #!!!注意 ONLY_FULL_GROUP_BY的语义就是确定select target list 中的所有列的值都是明确语义,简单的说来,在ONLY_FULL_GROUP_BY模式下,target list 中的值要么是来自于聚集函数的结果,要么是来自于group by list 中的表达式的值。 #设置sql_mole如下操作(我们可以去掉ONLY_FULL_GROUP_BY模式): mysql> set global sql_mode = 'STRICT_TRANS_TABLES,NO_ZERO_IN_DATE,NO_ZERO_DATE,ERROR_FOR_DIVISION_BY_ZERO,NO_AUTO_CREATE_USER,NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION' ; 查询岗位名以及岗位包含的所有员工名字 select post,group_concat(name) from employee group by post; 查询岗位名以及各岗位内包含的员工个数 select post,count( id ) from employee group by post; 查询公司内男员工和女员工的个数 select sex,count( id ) from employee group by sex; 查询岗位名以及各岗位的平均薪资 select post,avg(salary) from employee group by post; 查询岗位名以及各岗位的最高薪资 select post, max (salary) from employee group by post; 查询男员工与男员工的平均薪资,女员工与女员工的平均薪资 select sex,avg(salary) from employee group by sex; |
6):HAVING过滤
- 1、!!!执行优先级从高到低:where > group by > having
- 2、Where 发生在分组group by之前,因而Where中可以有任意字段,但是绝对不能使用聚合函数。
- 3、Having发生在分组group by之后,因而Having中可以使用分组的字段,无法直接取到其他字段,可以使用聚合函数
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | 查询各岗位内包含的员工个数小于 2 的岗位名、岗位内包含员工名字、个数 select post,group_concat(name),count( id ) from employee group by post having count( id ) < 2 ; 查询各岗位平均薪资大于 10000 的岗位名、平均工资 select post,avg(salary) from employee group by post having avg(salary) > 10000 ; 查询各岗位平均薪资大于 10000 且小于 20000 的岗位名、平均工资 select post,avg(salary) from employee group by post having avg(salary) > 10000 and avg(salary) < 20000 ; |
7):查询排序:ORDER BY
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 | 按单列排序 SELECT * FROM employee ORDER BY salary; SELECT * FROM employee ORDER BY salary ASC; #升序 SELECT * FROM employee ORDER BY salary DESC; #降序 按多列排序:先按照age排序,如果年纪相同,则按照薪资排序 SELECT * from employee ORDER BY age, salary DESC; 查询所有员工信息,先按照age升序排序,如果age相同则按照hire_date降序排序 select * from employee ORDER BY age asc,hire_date desc; 查询各岗位平均薪资大于 10000 的岗位名、平均工资,结果按平均薪资升序排列 select post,avg(salary) from employee group by post having avg(salary) > 10000 order by avg(salary) asc; 查询各岗位平均薪资大于 10000 的岗位名、平均工资,结果按平均薪资降序排列 select post,avg(salary) from employee group by post having avg(salary) > 10000 order by avg(salary) desc; |
8):限制查询的记录数:LIMIT
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | SELECT * FROM employee ORDER BY salary DESC LIMIT 3 ; #默认初始位置为0 SELECT * FROM employee ORDER BY salary DESC LIMIT 0 , 5 ; #从第0开始,即先查询出第一条,然后包含这一条在内往后查5条 SELECT * FROM employee ORDER BY salary DESC LIMIT 5 , 5 ; #从第5开始,即先查询出第6条,然后包含这一条在内往后查5条 |
9):使用正则表达式查询
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | SELECT * FROM employee WHERE name REGEXP '^ale' ; SELECT * FROM employee WHERE name REGEXP 'on$' ; SELECT * FROM employee WHERE name REGEXP 'm{2}' ; 小结:对字符串匹配的方式 WHERE name = 'egon' ; WHERE name LIKE 'yua%' ; WHERE name REGEXP 'on$' ; 查看所有员工中名字是jin开头,n或者g结果的员工信息 select * from employee where name regexp '^jin.*[gn]$' ; |
10):练习
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 | 查询每个部门最新入职的那位员工 #链表方式: SELECT * FROM employee AS t1 INNER JOIN ( SELECT post, max (hire_date) max_date FROM employee GROUP BY post ) AS t2 ON t1.post = t2.post WHERE t1.hire_date = t2.max_date; |
②多表
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 | #建表 create table department( id int , name varchar( 20 ) ); create table employee( id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar( 20 ), sex enum( 'male' , 'female' ) not null default 'male' , age int , dep_id int ); #插入数据 insert into department values ( 200 , '技术' ), ( 201 , '人力资源' ), ( 202 , '销售' ), ( 203 , '运营' ); insert into employee(name,sex,age,dep_id) values ( 'egon' , 'male' , 18 , 200 ), ( 'alex' , 'female' , 48 , 201 ), ( 'wupeiqi' , 'male' , 38 , 201 ), ( 'yuanhao' , 'female' , 28 , 202 ), ( 'liwenzhou' , 'male' , 18 , 200 ), ( 'jingliyang' , 'female' , 18 , 204 ) ; #查看表结构和数据 mysql> desc department; mysql> desc employee; mysql> select * from department; mysql> select * from employee; |
1):多表连接查询
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | #重点: SELECT 字段列表 FROM 表 1 INNER|LEFT|RIGHT JOIN 表 2 ON 表 1. 字段 = 表 2. 字段; #示例1:以内连接的方式查询employee和department表,并且employee表中的age字段值必须大于25,即找出年龄大于25岁的员工以及员工所在的部门 select employee.name,department.name from employee inner join department on employee.dep_id = department. id where age > 25 ; #示例2: select employee. id ,employee.name,employee.age,department.name from employee,department where employee.dep_id = department. id and age > 25 order by age asc; |
2):交叉连接
- 不适用任何匹配条件。生成笛卡尔积
- select * from employee,department;
3):内连接只连接匹配的行inner join
- 找两张表共有的部分,相当于利用条件从笛卡尔积结果中筛选出了正确的结果
- select employee.id,employee.name,employee.age,employee.sex,department.name from employee inner join department on employee.dep_id=department.id; #推荐这样写
- select employee.id,employee.name,employee.age,employee.sex,department.name from employee,department where employee.dep_id=department.id;#效果一样
4):外链接之左连接:优先显示左表全部记录left join
- 以左表为准
- 本质就是:在内连接的基础上增加左边有右边没有的结果
- select employee.id,employee.name,department.name as depart_name from employee left join department on employee.dep_id=department.id;
5):外链接之右连接:优先显示右表全部记录right join
- 以右表为准
- 本质就是:在内连接的基础上增加右边有左边没有的结果
- select employee.id,employee.name,department.name as depart_name from employee right join department on employee.dep_id=department.id;
6):全外连接:显示左右两个表全部记录
- 全外连接:在内连接的基础上增加左边有右边没有的和右边有左边没有的结果
- 注意:mysql不支持全外连接 full JOIN
- 强调:mysql可以使用此种方式间接实现全外连接
- select * from employee left join department on employee.dep_id = department.id union select * from employee right join department on employee.dep_id = department.id;
- #注意 union与union all的区别:union会去掉相同的纪录
7):子查询
- 1:子查询是将一个查询语句嵌套在另一个查询语句中。
- 2:内层查询语句的查询结果,可以为外层查询语句提供查询条件。
- 3:子查询中可以包含:IN、NOT IN、ANY、ALL、EXISTS 和 NOT EXISTS等关键字
- 4:还可以包含比较运算符:= 、 !=、> 、< 等
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 | #查询平均年龄在25岁以上的部门名 select id ,name from department where id in (select dep_id from employee group by dep_id having avg(age) > 25 ); #查看技术部员工姓名 select name from employee where dep_id in (select id from department where name = '技术' ); #查看不足1人的部门名(子查询得到的是有人的部门id) select name from department where id not in (select distinct dep_id from employee); #比较运算符:=、!=、>、>=、<、<=、<> #查询大于所有人平均年龄的员工名与年龄 select name,age from emp where age > (select avg(age) from emp); #查询大于部门内平均年龄的员工名、年龄 select t1.name,t1.age from emp t1 inner join (select dep_id,avg(age) avg_age from emp group by dep_id) t2 on t1.dep_id = t2.dep_id where t1.age > t2.avg_age; |
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | 8 ):补充EXISTS EXISTS关字键字表示存在。在使用EXISTS关键字时,内层查询语句不返回查询的记录。 而是返回一个真假值。 True 或 False 当返回 True 时,外层查询语句将进行查询;当返回值为 False 时,外层查询语句不进行查询 #department表中存在dept_id=203,Ture mysql> select * from employee - > where exists - > (select id from department where id = 200 ); #department表中存在dept_id=205,False mysql> select * from employee - > where exists - > (select id from department where id = 204 ); Empty set ( 0.00 sec) |
二、权限管理
1、授权表;
- user 针对:所有数据,所有库下所有表,以及表下的所有字段
- db 针对:某一数据库,该数据库下的所有表,以及表下的所有字段
- tables_priv 针对:某一张表,以及该表下的所有字段
- columns_priv 针对:某一个字段
2、授权(对库,对表,对字段);
- 查看帮助:help grant
- 常用权限有:select,update,alter,delete
- all可以代表除了grant之外的所有权限
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 | grant select,insert,update on db1. * to 'tom' @ '%' ; grant select,insert,update on db1.t1 to 'tom' @ '%' ; grant all privileges on db1.t1 to 'tom' @ '%' ; #针对所有库的授权:*.* grant select on * . * to 'tom' @ 'localhost' identified by '123' ; #只在user表中可以查到tom用户的select权限被设置为Y #针对某一数据库:db1.* grant select on db1. * to 'tom' @ '%' identified by '123' ; #只在db表中可以查到tom用户的select权限被设置为Y #针对某一个表:db1.t1 grant select on db1.t1 to 'tom' @ '%' identified by '123' ; #只在tables_priv表中可以查到tom用户的select权限 #针对某一个字段: grant select ( id ,name),update (age) on db1.t3 to 'tom' @ 'localhost' identified by '123' ; #可以在tables_priv和columns_priv中看到相应的权限 select * from tables_priv where user = 'tom' \G select * from columns_priv where user = 'tom' \G #查看权限 show grants for 'tom' @ '%' ; #删除权限 revoke all privileges on db1.t1 from 'tom' @ '%' ; revoke select on db1. * from 'tom' @ '%' ; |